# 责任链模式ChainOfResponsibility
阅读量 loading
# 一、概念
# 1、定义
为请求创建一个接收此次请求对象的链。
# 2、类型
行为型
# 3、适用场景
一个请求的处理需要多个对象当中的一个或几个协作处理
# 4、优点
- 请求的发送者和接受者(请求的处理者)解耦
- 责任链可以动态组合
# 5、缺点
- 责任链太长或者处理时间过长,影响性能
- 责任链有可能过多
# 6、相关设计模式
- 责任链模式和状态模式
责任链模式中各个对象并不指定下一个处理的对象是谁,只有在客户端设计链条中的顺序以及元素,直到被某个责任链条处理或者整个链条结束。状态模式是让每个状态对象知道自己下一个处理的对象是谁。
# 二、应用
现在模拟课程发布的一个应用场景。首先是课程类:
public class Course {
private String name;
private String article;
private String video;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getArticle() {
return article;
}
public void setArticle(String article) {
this.article = article;
}
public String getVideo() {
return video;
}
public void setVideo(String video) {
this.video = video;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
审批者类:
public abstract class Approver {
protected Approver approver;
public void setNextApprover(Approver approver) {
this.approver = approver;
}
public abstract void deploy(Course course);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
再创建一个手机的审批者和视频的审批者:
public class ArticleApprover extends Approver {
@Override
public void deploy(Course course) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(course.getArticle())) {
System.out.println(course.getName() + "含有手记,批准");
if (approver != null) {
approver.deploy(course);
}
} else {
System.out.println(course.getName() + "不含有手记,不批准,流程结束");
return;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class VideoApprover extends Approver {
@Override
public void deploy(Course course) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(course.getArticle())) {
System.out.println(course.getVideo() + "含有视频,批准");
if (approver != null) {
approver.deploy(course);
}
} else {
System.out.println(course.getVideo() + "不含有视频,不批准,流程结束");
return;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
类图:
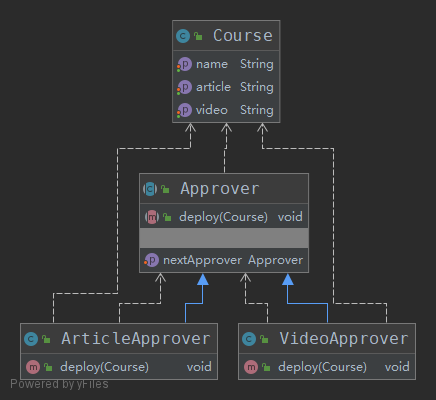
测试类:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Approver articleApprover = new ArticleApprover();
Approver videoApprover = new VideoApprover();
Course course = new Course();
course.setName("设计模式");
course.setArticle("设计模式手机");
course.setVideo("设计模式视频");
articleApprover.setNextApprover(videoApprover);
articleApprover.deploy(course);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
执行结果:
设计模式含有手记,批准
设计模式视频含有视频,批准
1
2
2
# 三、源码中的应用
# Filter
javax.servlet 包下的 Filter 接口有一个 doFilter() 方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
1
2
2
其中的 FilterChain 参数:
public interface FilterChain {
/**
* Causes the next filter in the chain to be invoked, or if the calling
* filter is the last filter in the chain, causes the resource at the end of
* the chain to be invoked.
*
* @param request
* the request to pass along the chain.
* @param response
* the response to pass along the chain.
*
* @since 2.3
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
FilterChain 中有很多 Filter,这些 Filter 按照一定逻辑顺序组装成一个链条。这就是责任链模式,具体的某一个 Filter 就是链条中的一个元素。实现 FilterChain 的接口 MockFilterChain,它是为了方便 Spring 测试或者 Mock 使用的。Filter 的实现就比较多了,例如:LoggerContextFilter,它的 doFilter() 方法:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
LoggerContext lc = (LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
ContextSelector selector = ContextSelectorStaticBinder.getSingleton().getContextSelector();
ContextJNDISelector sel = null;
if (selector instanceof ContextJNDISelector) {
sel = (ContextJNDISelector)selector;
sel.setLocalContext(lc);
}
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} finally {
if (sel != null) {
sel.removeLocalContext();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20