# 策略模式Strategy
# 一、概念
# 1、定义
定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以互相替换,此模式让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的用户。
# 2、扩展
if else 的代码可以通过策略模式消除掉。
# 3、类型
行为型
# 4、适用场景
- 系统有很多类,而他们的区别仅仅在于他们的行为不同
- 一个系统需要动态的在几种算法中选择一种
# 5、优点
- 满足开闭原则
- 避免使用多重条件转移语句
- 提高算法的保密性和安全性
# 6、缺点
- 客户端必须知道所有的策略类,并自行决定使用哪一个策略类
- 产生很多策略类
# 7、相关设计模式
- 策略模式和工厂模式
工厂模式是创建型的设计模式,接受指令,创建符合要求的具体对象;策略模式是行为型的设计模式,接受已经创建好的对象,从而实现不同的行为
- 策略模式和状态模式
策略模式中客户端需要知道选择哪个策略;状态模式中客户端不需要关系具体的状态,这些状态会自动转换。在不同状态下,如果行为有差异,而且状态可以发生转换时,可以使用状态模式。如果某个行为存在多种实现方式,可以使用策略模式。
# 二、应用
在各个购物节的时候都有各种各样的促销,这里定义一个促销接口:
public interface PromotionStrategy {
void doPromotion();
}
2
3
4
分别有3个具体的实现:满减促销、立减促销和返现促销。
public class FullReductionPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy{
@Override
public void doPromotion() {
System.out.println("满减促销");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class DirectReductionPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy{
@Override
public void doPromotion() {
System.out.println("立减促销");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class ReturnCashPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy{
@Override
public void doPromotion() {
System.out.println("返现促销");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
在新建一个活动,活动接受一个促销策略作为参数传入构造方法中:
public class PromotionActivity {
private PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy;
public PromotionActivity(PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy) {
this.promotionStrategy = promotionStrategy;
}
public void executePromotionStrategy() {
promotionStrategy.doPromotion();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
此时的类图:
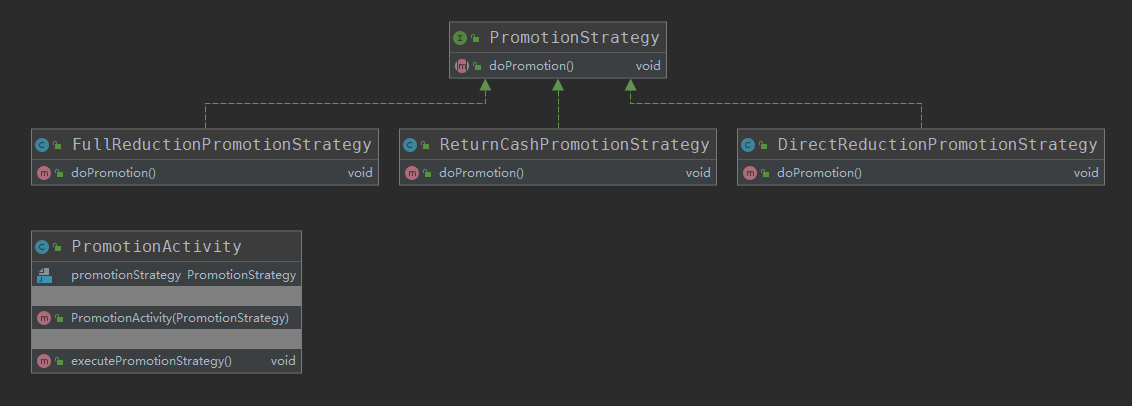
应用层:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PromotionActivity promotionActivity618 = new PromotionActivity(new DirectReductionPromotionStrategy());
PromotionActivity promotionActivity1111 = new PromotionActivity(new ReturnCashPromotionStrategy());
promotionActivity618.executePromotionStrategy();
promotionActivity1111.executePromotionStrategy();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
执行结果:
立减促销
返现促销
2
如果此时需要一个新的策略也非常简单,直接新建一个策略,然后传入到具体的活动中即可。
实际应用中的代码可能会这么写:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PromotionActivity promotionActivity;
String promotionKey = "FullReduction";
if (StringUtils.equals(promotionKey, "FullReduction")) {
promotionActivity = new PromotionActivity(new FullReductionPromotionStrategy());
} else if (StringUtils.equals(promotionKey, "DirectReduction")) {
promotionActivity = new PromotionActivity(new DirectReductionPromotionStrategy());
} else {
promotionActivity = new PromotionActivity(new ReturnCashPromotionStrategy());
}
promotionActivity.executePromotionStrategy();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
前端传过来一个条件,根据这个条件判断采用哪种促销,然后使用执行:
满减促销
但是这么做,还是要写很多 if else 语句。那么如何消除掉这部分代码呢?
首先创建一个促销工厂:
public class PromotionStrategyFactory {
private static Map<String, PromotionStrategy> PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.put(PromotionKey.FULL_REDUCTION, new FullReductionPromotionStrategy());
PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.put(PromotionKey.DIRECT_REDUCTION, new DirectReductionPromotionStrategy());
PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.put(PromotionKey.RETURN_CASH, new ReturnCashPromotionStrategy());
}
private static final PromotionStrategy EMPTY_PROMOTION_STRATEGY = new EmptyPromotionStrategy();
private PromotionStrategyFactory() {
}
public static PromotionStrategy getPromotionStrategy(String promotionKey) {
PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy = PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.get(promotionKey);
return promotionStrategy == null ? EMPTY_PROMOTION_STRATEGY : promotionStrategy;
}
private interface PromotionKey {
String FULL_REDUCTION = "FullReduction";
String DIRECT_REDUCTION = "DirectReduction";
String RETURN_CASH = "ReturnCash";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
当没有匹配到任何促销策略的时候,这里会返回一个空的促销策略。这个空的促销策略:
public class EmptyPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
@Override
public void doPromotion() {
System.out.println("无促销");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
那么此时的应用层就是这样子的:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String promotionKey = "DirectReduction";
PromotionActivity promotionActivity = new PromotionActivity(
PromotionStrategyFactory.getPromotionStrategy(promotionKey));
promotionActivity.executePromotionStrategy();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
执行结果:
立减促销
# 三、源码中的应用
# 1、Comparator
Comparator 比较器接口就相当于一个策略,它有2个方法需要实现:
int compare(T o1, T o2);
boolean equals(Object obj);
2
3
那这个策略在哪里使用呢?
Arrays 类有这么一个方法:
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex, c);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
它的最后一个参数就接收一个比较器,并且在按照这比较逻辑,在方法内部一步一步往下传。
# 2、TreeMap
TreeMap 有这样一个比较器的成员变量:
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
内部还将这个比较器进行了加工:
final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {
return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2)
: comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);
}
2
3
4
# 3、Spring 中的 Resource
在 org.springframework.core.io 包中的 Resource 类,它的实现类例如 ClassPathResource、FileSystemResource、PathResource、UrlResource 等等。这个 Resource 接口就相当于一个策略的抽象,这些实现类就是具体的行为。
# 4、Spring 中的 InstantiationStrategy
InstantiationStrategy 这个接口是 Spring 在初始化 Bean 的时候的一个策略接口,具体的实现类是 SimpleInstantiationStrategy 和 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy,SimpleInstantiationStrategy 在原来 InstantiationStrategy 接口中又新增了2个方法,并且它还是 CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy 的父类。