# 简单工厂SimpleFactory
# 一、概念
# 1、定义
由一个工厂对象决定创建出哪一种产品类的实例
# 2、类型
创建型(不属于GOF23种设计模式)
# 3、适用场景
- 工厂类负责创建的对象比较少
- 客户端(应用层)只知道传入工厂类的参数,对于如何创建对象(逻辑)不关心
# 4、优点
只需要传入一个正确的参数,就可以获取所需要的对象而无须知道其创建细节
# 5、缺点
工厂类的职责相对过重,增加新的产品需要修改工厂类的判断逻辑,违背开闭原则
# 二、应用
首先创建一个视频类,它有一个生产的方法,因为每个视频的生产过程都是不一样的,所以这里定义为抽象方法,交由子类实现:
public abstract class Video {
public abstract void produce();
}
2
3
4
Java视频类继承 Video 类:
public class JavaVideo extends Video {
@Override
public void produce() {
System.out.println("录制Java课程视频");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
Python视频类继承 Video 类:
public class PythonVideo extends Video {
@Override
public void produce() {
System.out.println("录制Python课程视频");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
应用层:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Video video = new JavaVideo();
video.produce();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
执行结果:
录制Java课程视频
此时的类图:
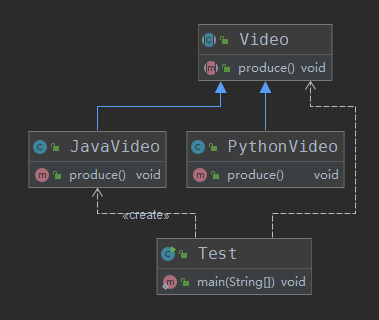
此时的应用层想要创建具体某种视频,是非常依赖具体视频类的,怎么才能够让应用层不依赖具体实现类呢?
现在把具体创建视频的功能移植到一个工厂中:
public class VideoFactory {
public Video getVideo(String type) {
if (type.equalsIgnoreCase("java")) {
return new JavaVideo();
}
if (type.equalsIgnoreCase("python")) {
return new JavaVideo();
}
return null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
根据具体传入的类型进行实例化对应的对象。
应用层:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
VideoFactory videoFactory = new VideoFactory();
Video video = videoFactory.getVideo("java");
if (video == null) {
return;
}
video.produce();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
调用工厂类时,只需要传递给工厂想要的类型,工厂就会创建出对应的视频。
运行结果:
录制Java课程视频
此时的类图:

可以看出,现在的应用层只依赖工厂类,即使有更多类型的视频需要创建,应用层也只会和工厂类打交道,告诉工厂需要什么视频,由工厂进行创建。
但是此时有个问题,如果后面有新的类型的视频需要创建,岂不是要修改工厂类的 if 判断,不行不行。我们需要优化。
优化后的工厂类:
public class VideoFactory {
public Video getVideo(Class c) {
Video video = null;
try {
video = (Video) Class.forName(c.getName()).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return video;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
将原来传 String 参数的方法改为了传具体的 Class 对象,修改后,如果产生新类型的视频,这个工厂类是不需要修改的,只需要确定好传入的 Class 对象就能正确的创建出来对象了。
再来看看应用层的变化:
public static void main(String[] args) {
VideoFactory videoFactory = new VideoFactory();
Video video = videoFactory.getVideo(JavaVideo.class);
if (video == null) {
return;
}
video.produce();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
运行结果:
录制Java课程视频
现在直接传入需要创建的视频的 class 对象就可以创建出对应类型的视频了。
# 三、源码中的应用
# 1、Calendar类
createCalendar(TimeZone zone, Locale aLocale) 方法内部有这样的代码:
if (aLocale.getLanguage() == "th" && aLocale.getCountry() == "TH") {
cal = new BuddhistCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else if (aLocale.getVariant() == "JP" && aLocale.getLanguage() == "ja"
&& aLocale.getCountry() == "JP") {
cal = new JapaneseImperialCalendar(zone, aLocale);
} else {
cal = new GregorianCalendar(zone, aLocale);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Calendar 类相关的类图:

# 2、JDBC 中加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
也是用到了简单工厂模式,当执行完上面的代码后,将 Driver 类加载到 JVM 中,然后就执行 Driver 类的静态代码:
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
然后调用 DriverManager 的 getConnection() 获取到连接:
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
/*
* When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
* (which is invoking this class indirectly)
* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
* can be loaded from here.
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// if we got here nobody could connect.
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
# 3、slf4j 中的 LoggerFactory
getLogger(String name) 方法:
public static Logger getLogger(String name) {
ILoggerFactory iLoggerFactory = getILoggerFactory();
return iLoggerFactory.getLogger(name);
}
2
3
4
这里列出 ILoggerFactory 的一个实现类 LoggerContext 对于 getLogger() 的实现:
public final Logger getLogger(String name) {
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name argument cannot be null");
} else if ("ROOT".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
return this.root;
} else {
int i = 0;
Logger logger = this.root;
Logger childLogger = (Logger)this.loggerCache.get(name);
if (childLogger != null) {
return childLogger;
} else {
int h;
do {
h = LoggerNameUtil.getSeparatorIndexOf(name, i);
String childName;
if (h == -1) {
childName = name;
} else {
childName = name.substring(0, h);
}
i = h + 1;
synchronized(logger) {
childLogger = logger.getChildByName(childName);
if (childLogger == null) {
childLogger = logger.createChildByName(childName);
this.loggerCache.put(childName, childLogger);
this.incSize();
}
}
logger = childLogger;
} while(h != -1);
return childLogger;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39